The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of fluids and electrolytes in our bodies, as well as filtering waste products from our blood. Early detection and treatment of kidney disease are vital to prevent further damage and complications. Thankfully, your body does send you signals that there could be something wrong with your kidneys. Learn what they are and listen to your body so that you can receive medical help as soon as possible.
Understanding the Role of the Kidneys
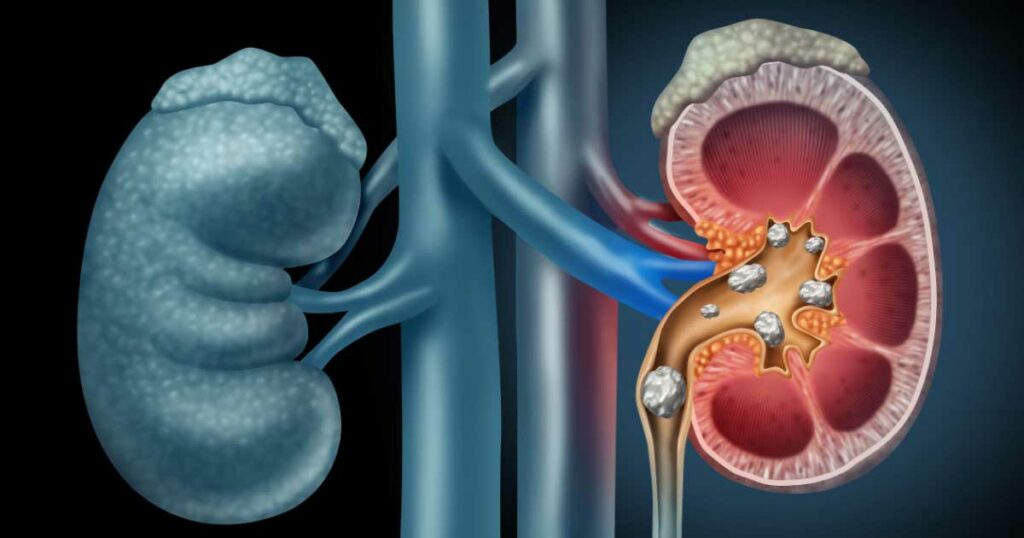
The kidneys are two small bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine, just below the ribcage. Their main function is to filter the blood, removing waste products, and excess fluids from the body. The kidneys also help control blood pressure, produce red blood cells, and maintain the balance of electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium. When the kidneys are healthy, they filter around 120 to 150 quarts of blood daily, producing about 1 to 2 quarts of urine.
What is Kidney Disease?
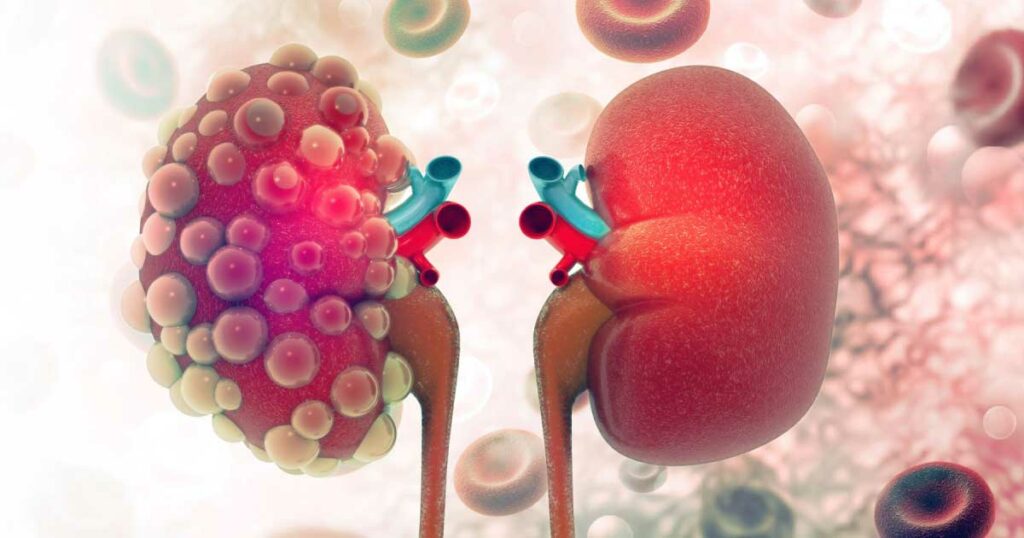
Kidney disease, also known as renal disease, occurs when the kidneys sustain damage and are no longer able to function optimally. There are various causes of kidney disease, including high blood pressure, diabetes, infections, autoimmune disorders, and genetic factors. Over time, kidney disease can progress and lead to kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant. Early detection is critical to prevent further damage and manage the condition effectively.
Signs of Kidney Disease
One of the hardest parts about kidney disease is that many people don’t catch it until it is already quite advanced. Thankfully, the body does send signs that the kidneys are in trouble. If you notice these, you can go to your healthcare practitioner to hopefully solve the problem before it becomes worse. These are 10 signs your body is telling you that your kidneys are in danger.
1. Changes in Urination

One of the earliest signs of kidney disease is changes in urine production. You may notice increased frequency of urination, especially during the night. On the other hand, you may experience decreased urination or foamy urine.
2. Fatigue and Weakness

Kidney disease can lead to anemia, a condition characterized by low red blood cell count. This can result in persistent fatigue, weakness, and difficulty concentrating.
3. Swelling

Excessive fluid buildup in the body, known as edema, commonly occurs with kidney disease. Swelling can affect the legs, hands, face, and even the abdomen.
4. Persistent Back Pain






